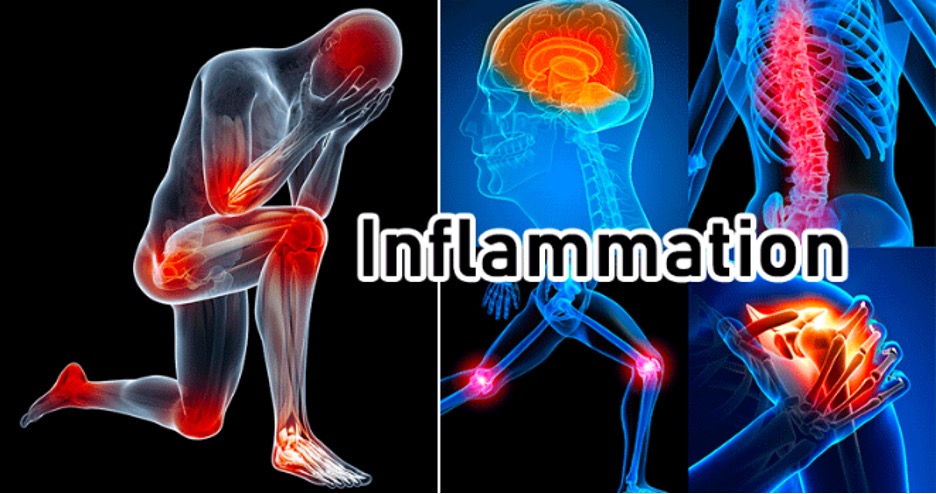
When your body is damaged or is exposed to a pathogen (such as viruses, bacteria, or dangerous chemicals), your immune system is activated.
Your immune system’s first line of defense are inflammatory cells and cytokines, molecules that cause the production of additional inflammatory cells.
In order to ingest pathogens and other hazardous things or to start repairing injured tissue, these cells trigger an inflammatory response. The symptoms might include pain, bruising, swelling, or redness. But inflammation can also affect internal body functions that are not evident.
How is inflammation pain treated?
Treatment is not usually necessary for inflammation. Rest, ice, and proper wound care may frequently reduce the pain associated with acute inflammation in a few of days.
If you have persistent inflammation, your doctor could advise:
Supplements: Some vitamins, including vitamins A, C, and D, as well as dietary supplements like zinc, may help to decrease inflammation and promote healing. For instance, your doctor could advise taking vitamin(s) or a fish oil supplement. Alternately, you might add spices like turmeric, ginger, or garlic that have anti-inflammatory qualities.
NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications These OTC medications reduce inflammation. Your doctor could advise Tapal 100mg & Tapidol 100mg as pain relievers.
Injections of corticosteroids: These doses reduce inflammation in a particular joint or muscle. For instance, if your back is affected by rheumatoid arthritis, your doctor can inject a steroid into your spine. The same body area shouldn’t have more than three to four steroid injections per year.
What are the differences between inflammation that is acute and chronic?
There are two types of inflammation:
Acute inflammation: The body’s response to a wound that develops quickly, as a fingernail cut. To hasten healing, your body releases inflammatory cells to the wound. These cells start the healing process.
Chronic inflammation: Your body continues to release inflammatory cells even when there is no external threat. For instance, inflammatory cells and chemicals attack the joint tissues in rheumatoid arthritis, resulting in an intermittent inflammation that can gravely damage joints and cause pain and deformity.
Associated item: Noosanta 100mg
What symptoms are present in both acute and chronic inflammation?
- Skin at the site of harm that has been flushed as a result of chronic inflammation.
- Or sympathy.
In comparison to acute inflammation, indications of chronic inflammation may be less obvious. •Abdominal ache is one symptom of chronic inflammation.
- Chest discomfort.
- (such as systemic lupus)
- (For example: tb)
Alternatively, joint stiffness. (such as rheumatoid arthritis)
Ulcers in the mouth. (such as a hiv infection)
What are the most common causes of inflammation?
The following are the most typical causes of chronic inflammation:
- Illnesses where your body assaults good tissue, like lupus.
- Exposure to poisons, such as industrial chemicals or pollution.
- Acute inflammation that is not being treated, such as from an infection or wound.
Inflammation in the body is also influenced by certain lifestyle variables. Chronic inflammation may be more likely to occur if you:
- Overindulge in booze.
- Unless it is due to being exceptionally muscular, have a high body mass index (bmi) that is within the ranges for obesity.
- You either don’t exercise enough or you exercise too frequently at your maximal effort.
- Have persistent tension.